Bio-based materials refer to materials derived from natural biomass, including materials that use biomass as raw materials or (and) obtained through biological manufacturing. Bio-based materials are derived from renewable resources and have many advantages such as carbon reduction and sustainability.
With the introduction of the concept of carbon neutrality, bio-based materials, and even bio-based degradable materials, have received widespread attention due to their good environmental protection characteristics. What is the current supply and demand status of bio-based materials? What are the downstream distributions? This article takes you to find out.
1. The EU market is in short supply, and bio-based materials have broad room for growth

Biomass raw materials instead of petroleum-based raw materials, the combination of biochemical methods or biological methods are the key directions for the development of the chemical manufacturing industry. Bio-based chemicals refer to products such as bulk chemicals and fine chemicals produced using renewable biomass (starch, glucose, lignocellulose, etc.) as raw materials.
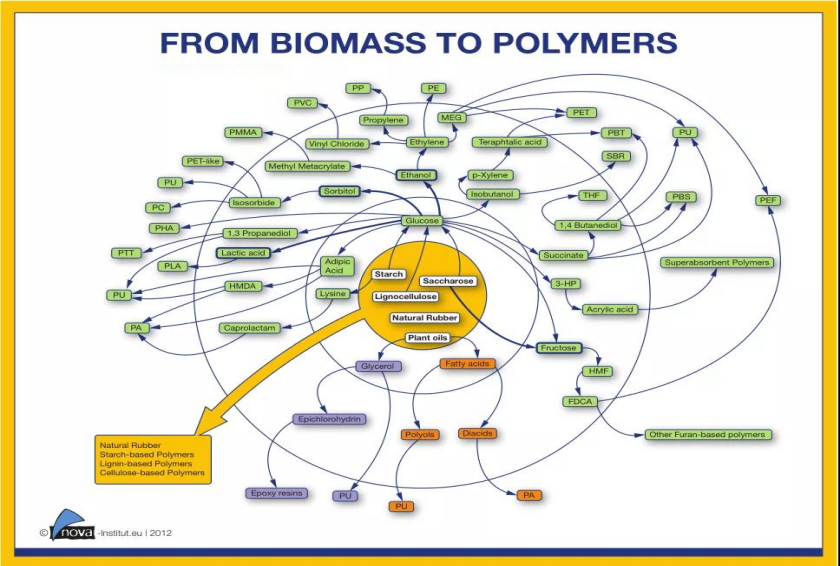
According to Nova Institute research, from a technical point of view, almost all industrial materials made from fossil resources can be replaced by bio-based materials. In recent years, advances in genomics, proteomics, metabolomics and systems biology related to biorefining technology have jointly constructed a biosynthetic network of chemicals and downstream materials.
In recent years, under the guidance of policies of various countries, the growth of biofuel production capacity has promoted the development of the biorefinery sector, while also accelerating the construction of the entire industrial chain of the agricultural sector-biorefining sector-downstream manufacturers-certification bodies-consumer sector. Drive the rapid development of downstream bio-based chemicals and new materials.
European bioeconomy has first-mover advantages. The RoadToBio project led by the European Union has planned a roadmap for the European chemical industry to move towards bioeconomy, with a view to realizing a diversified bio-based product portfolio.
The RoadToBio project subdivides bio-based products, including bulk chemicals, solvents, polymers for plastics, chemical fiber products, paints/coatings/inks/dyes, surfactants, cosmetics and personal care products, adhesives, lubricants, and plasticizers agents and other fields.
As one of the world's largest consumer markets for bio-based chemicals and downstream materials, the EU has a large audience for products under the official long-term policy publicity. The EU bio-based product categories include 10 major categories (excluding biofuels) such as bulk chemicals, plastics, solvents, and surfactants. Among them, bulk chemicals and solvents are all basic chemicals, surfactants, personal care/cosmetics, adhesives, lubricants and plasticizers are all fine chemicals, and paints/coatings/inks/dyes, plastics and fiber products belong to Bio-based polymers.
In 2018, the EU market's bio-based chemicals and downstream output was nearly 4.7 million tons, the demand was nearly 5.5 million tons, and the output value was nearly 9.2 billion euros. There is a strong demand for bio-based products in the high-end consumer market. Among the series of bio-based products, surfactants, paints/coatings/inks/fuels, fiber products and personal care/cosmetics have the largest output, which is attributed to the higher level of consumption in the EU market and the large demand for bio-based oil and fat compounds .
In terms of price, limited by the scale of production in the region, the price of bio-based basic chemicals is higher than that of petroleum-based products at this stage. As product categories become more refined, the closer to the end consumer, the lower the product price. The price gap is slowly narrowing.
With the rapid progress of biosynthetic technology, the selling price of some bio-based fine chemicals (such as succinic acid, PA56) is even lower than the corresponding petrochemical products.
The penetration rate of bio-based chemicals and downstream in the EU market is only 3%, and the future market growth space is 4 times, and the global market is expected to exceed 100 billion. According to JRC data, the total production of chemicals in the EU's corresponding sub-sectors in 2018 was nearly 160 million tons per year, and the proportion of bio-based chemicals was only 3%, especially in the bulk chemicals and plastics industries, where the total output accounted for 77%, and the substitution rate of bio-based only 0.7%.
According to the EU's "Industrial Biotechnology Vision Plan", the minimum replacement rate of 6% for bulk chemicals and plastic products and 30% for fine chemicals is estimated. By 2030, the output value of bio-based products will reach 37 billion euros per year. Compared with the output value of 9.2 billion euros in 2018, there is room for growth of 4 times.
According to JRC data, the amount of new private investment in the above sub-sectors is expected to reach 19 billion Euros from 2018 to 2025. When combined with the EU's bioeconomy special plan investment that has continued to increase in recent years, there is a lot of room for the future bio-based product replacement rate.
In addition to the EU market, the bioeconomy strategies of the United States and China are also being vigorously implemented. Assuming that the market size is equivalent to that of the EU, the global bio-based chemicals and downstream market is expected to reach the level of 100 billion euros in the future.
2. There are many bio-based chemicals and downstream tracks
The output of bio-based chemicals has grown rapidly in recent years. According to estimates by IEA Bioenergy, the total output of bio-based chemicals in 2019 will be nearly 10 million tons per year (excluding fuel ethanol), with a compound growth rate of nearly 10% from 2011 to this year.
At present, the world's major bulk bio-based chemicals include ethylene, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, glycerin, butylene glycol, lactic acid, sebacic acid, etc., and biosynthetic technology has been industrialized.
Among them, the sugar-based compounds ethylene, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, lactic acid, butylene glycol, succinic acid, pentane diamine, etc. are the key raw materials for downstream bio-based PE, PLA, PET, PBS, PTT and PBAT. The oil-based compounds glycerin, long-chain fatty acids and fatty acids are used in the preparation of bio-based PHA, PA and epoxy resins.
3. Bio-based plastics: emerging markets are at the starting point of rapid growth
Bio-based plastics are currently the most important application field for downstream materials of bio-based chemicals.
As the name implies, bio-based plastics refer to new materials whose raw materials are wholly or partly derived from biomass (corn, sugar cane, cellulose, etc.). According to whether it can be decomposed into small molecular compounds by microorganisms (bacteria, molds, algae, etc.) under certain conditions, bio-based plastics are divided into two types: biodegradable and non-biodegradable plastics.
According to European Bioplastics data, bio-based polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), polylactic acid (PLA), polybutylene succinate (PBS), adipic acid/butylene terephthalate (PBAT) and starch-based plastics are both biodegradable plastics.
And bio-based polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), propylene terephthalate (PTT), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), nylon (PA) series and polyethylene furanate ( PEF) etc. are not biodegradable.
Bio-based plastic products have two main advantages:
(1) Excellent emission reduction ability, the CO2 emission of bioplastics is only 20% of that of traditional plastics
(2) Some plastics are naturally biodegradable, and non-degradable bio-based plastics can also be recycled and reused
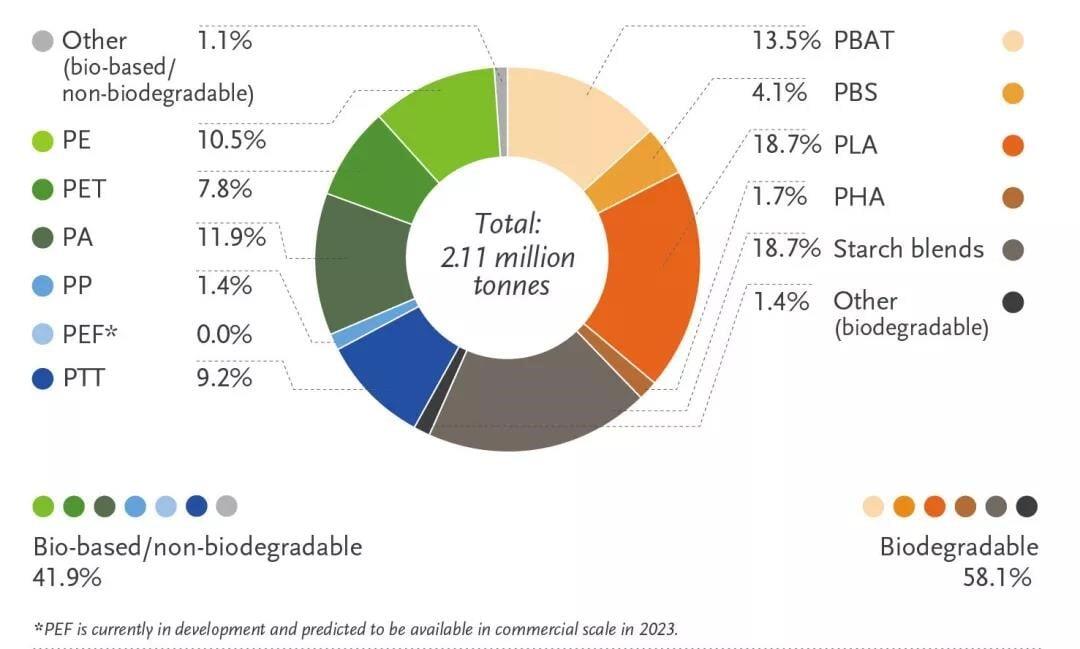
According to European Bioplastics data, the global production of plastics in 2018 was nearly 360 million tons, while the output of bio-based plastics in 2020 was nearly 2.11 million tons, accounting for less than 1%. In recent years, with the growth of demand and the emergence of more and more bio-based polymers, applications and products, the bioplastics market has continued to grow.
According to MarketsandMarkets forecasts, the global bioplastics and polymers market is expected to be worth USD 10.5 billion in 2020. Driven by the industrial support policies of various governments, it is expected to grow to USD 27.9 billion in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 21.7%.
The top five bio-based plastics in the world are starch-based plastics (19%), PLA (19%), PA (12%), PE (11%), and PTT (9%). PBAT (13%) accounts for nearly 80% of total production.
In terms of regional distribution, Europe is the main hub of the entire bioplastics industry and a relatively mature area for bioplastics development. It occupies a pivotal position in the research and development of bioplastics and is the world's largest industry market. However, the market growth rate of bioplastics in Europe is relatively low. The output in 2020 will account for 26%, which is lower than 46% in the Asia-Pacific region.
The Asia-Pacific region is an emerging market. As a major production center, about 70% of the world's injection molding infrastructure is located in Asia, so the market is growing at the fastest rate. North and South America totaled 27%. In recent years, the output has increased year-on-year, and the market space is large. It is a bright spot for the promotion of bioplastics in the future.
4. In recent years, the application scope of bio-based plastics has become more and more diversified
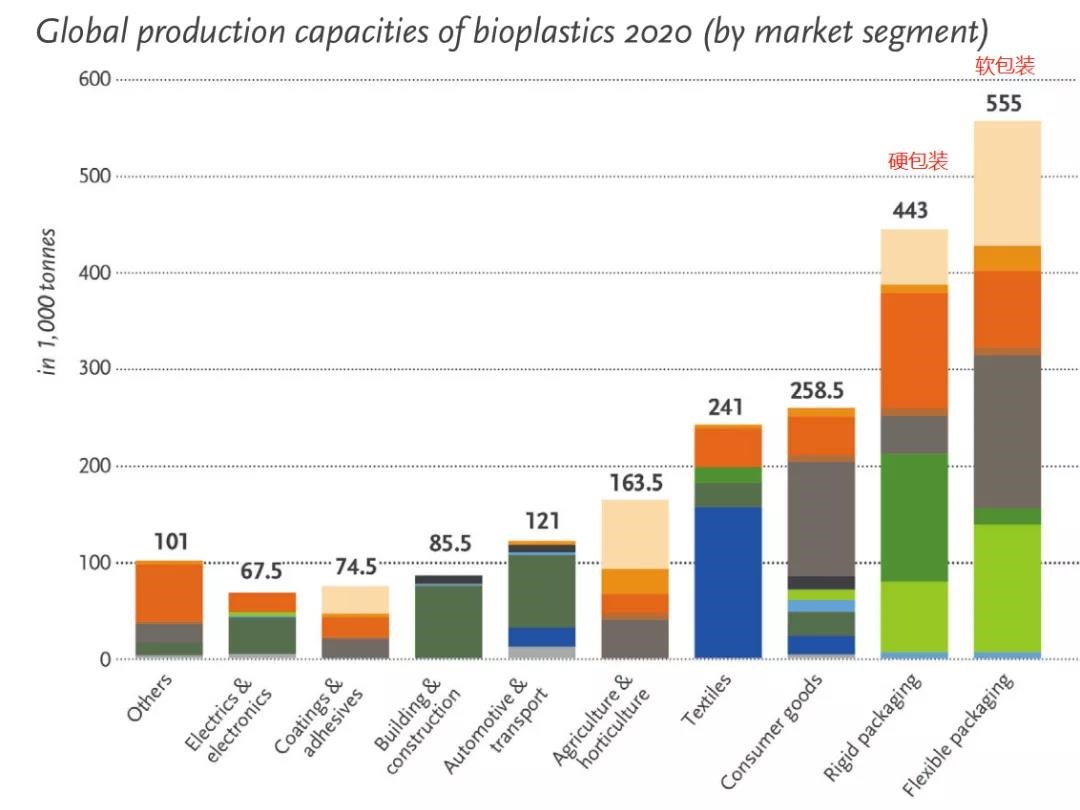
Bio-based plastics are mainly used in packaging (hard packaging, soft packaging), textiles, automobiles and transportation, consumer goods, agriculture and gardening, coatings and adhesives, building and construction, electronics and electrical appliances, and other industries. Bioplastics are suitable for packaging industry due to their good gloss, good barrier, electrical resistance and printing properties. Therefore, the packaging industry is the largest application field of bioplastics, accounting for about 47% of the total bioplastics market, nearly 1 million tons.
Bio-based PET accounts for the largest proportion of bioplastics used in rigid packaging. For example, all beverages of Coca-Cola are packaged in PET bottles, while bioplastics used in flexible packaging account for the largest proportion of biodegradable starch mixtures.
The bioplastics used in textiles account for about 11% of the total bioplastics, and the largest proportion is PTT. The largest proportion of bioplastics used in automobiles and transportation is bio-based PA. It is worth mentioning that PLA also has many applications in packaging and textile fields due to its good use performance and processing performance. Bio-based plastics have a wide range of applications, and their market prospects are very impressive.