Liu Jing, professor of environmental biotechnology at Lund University in Sweden and executive director of Bipu Instruments, introduced commonly used biodegradability test methods and technologies, evaluated and compared various technologies, and pointed out that there will be a lot of degradation tests in the future. What needs to be done is a detection method that minimizes manpower consumption.
1. Aerobic biodegradability test method
Aquatic (fresh water) aerobic biodegradation:
ISO 14851 (plastics) → national standard GB/T 19276.1; ISO 14852 (plastics) → national standard GB/T 19276.2; ASTM D5209 (plastics); JIS K 6951 (plastics)
ISO 9439 (organic compounds); ISO 14593 (organic compounds); OECD 301 A&F (compounds); EN 14047 (packaging materials)
Aquatic (sea water) aerobic biodegradation:
ISO 18830 (non-floating plastic)→national standard GB/T 40611; ISO 19679 (non-floating plastic)→national standard GB/T 40612; ISO 22404 (non-floating plastic)→national standard GB/T 40367; ISO 23977-1&2 ( plastic)
Soil biodegradation:
ISO 17556 (plastics)→National standard GB/T 22047; ASTM 5988 (plastics)
ISO 11266 (organic compounds); ISO 23517 (agricultural mulch)
Composting environment composting biodegradation:
Industrial composting test standard controlled composting biodegradation Test: ISO 14855-1 (plastics) → national standard GB/T 12771; ISO 14855-2 (plastics) → national standard GB/T 19277.2; ASTM D5338 (plastics); EN 14046 (packaging material); JIS K 6953 (plastic)
Mineral Bed Composting Test: ISO 14855-1 (plastic); ISO 14855-2 (plastic)
Radio-labelled 14C-atoms Composting biodegradation test: ASTM D6340 (Cancelled)
2. Anaerobic biodegradability test method
Aquatic anaerobic biodegradation:
ISO 14853 (plastic) →National standard GB/T 32106
Controlled slurry digestion system:
ISO 13975 (plastic)→National Standard GB/T 38737
ASTM D5210 (plastics); ISO 11734 (organic compounds); OCED 311 (organic compounds)
High-solids anaerobic digestion conditions:
ISO 15985 (plastics) >National Standard GB/T 33797; ASTM D5511 (plastics)
Landfill anaerobic digestion environment accelerated landill:
ASTM D5526 (plastic); ASTM D5525 (plastic)
3. Aerobic biodegradability detection technology
By measuring the oxygen demand in the airtight respirometer:
directly detect oxygen consumption through a pneumatic airtight respirator
By measuring the amount of carbon dioxide released:
First, the alkaline solution is adsorbed, and then the fixed CO2 is measured: dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), barium hydroxide titration, conductivity, gravimetric method, etc.
Direct measurement, such as simultaneous measurement of carbon dioxide concentration and gas flow by infrared analyzer and flow meter.
The more the detection, the more the error. In all detection methods, the most ideal situation is to reduce the detection steps. The simpler the steps, the smaller the error of the data obtained theoretically.
4. Anaerobic biodegradability detection technology
By measuring the released biogas (mixture of methane and carbon dioxide):
Pressure method to calculate gas volume
Volume method, volume method directly measure volume

5. Analysis of advantages and disadvantages of detection technology
Each detection technology has its own advantages and disadvantages. How to evaluate them? Based on his years of industry experience, Professor Liu listed several key evaluation factors: environmental factors (temperature, pressure, water vapor), data quality (precision, accuracy, etc.), manpower consumption, user-friendliness, system complexity degree.
First look at the influence of environmental factors, because the detection is generally a gas, and the gas is affected by temperature, pressure and even gas composition. For example, changes in the ambient temperature will cause the gas to expand or contract.
In addition, data quality, manpower consumption, and user-friendliness are also very important, because in the future, with the implementation of bans and restrictions on plastics in various countries, the development of new materials is crucial, and not only the degradability of new materials needs to be tested, but the final product The biodegradability of the product also needs to be evaluated, because the degradability of the product is not necessarily the same as the degradability of the raw material.
In other words, there will be a lot of tests in the future. If future tests are still time-consuming, labor-intensive and user-friendly, it is undoubtedly not feasible in the actual operation process. Therefore, in order to meet future testing needs, what we have to do is to reduce the manpower consumption as much as possible, the user-friendliness is good, the amount of data needs to be large, and the detection method needs to be high in accuracy.
The following is a comparative evaluation of various detection technologies:
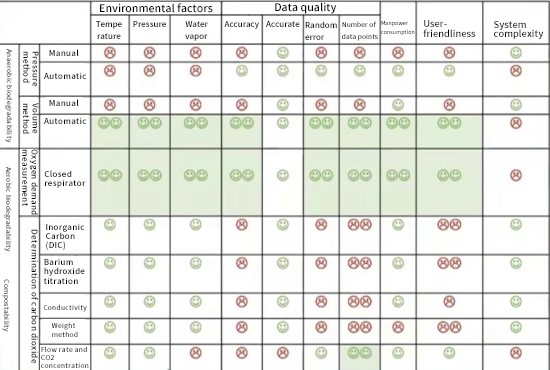
Professor Liu believes that automated and high-precision equipment will have a better prospect to deal with a large number of tests. In terms of detection technology, in terms of personal experience, he prefers to use volumetric method for anaerobic biodegradation determination, and to use closed respirator for aerobic biodegradation determination.

