Carbon sinks, carbon allowances, carbon trading, CCUS, CCER, carbon knowledge!
Today I will mainly sort out the terms and concepts behind carbon neutrality, carbon trading, and carbon allowances. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
The process of carbon trading can be described as follows with a simple example:

What is carbon emissions?
Carbon emission refers to the process of emitting greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, etc.) to the outside world during human production and business activities.
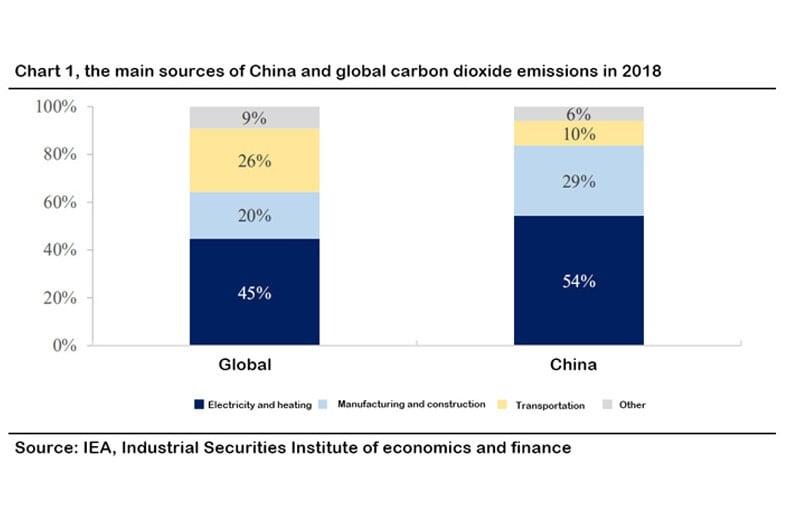
Carbon emissions are currently considered to be one of the main causes of global warming. The largest proportion of our country's carbon emissions (54%) comes from the burning of fossil fuels in the production process of the electricity and heating sectors.
What is carbon peak?
In a broad sense, carbon peak refers to a certain point in time when carbon dioxide emissions no longer increase and reach a peak, and then gradually fall back. According to the introduction of the World Resources Institute, carbon peaking is a process, that is, carbon emissions first enter a plateau period and can fluctuate within a certain range, and then enter a stage of steady decline.
Carbon peaking is a prerequisite for achieving carbon neutrality, and achieving carbon peaking as soon as possible can promote the early realization of carbon neutrality. Based on this, combined with the time node of my country's commitments: 1) From now to 2030, my country's carbon emissions will still be in a ramp-up period; 2) During the 20 years from 2030 to 2060, carbon emissions will have to pass the plateau period and finally complete the emission reduction task.
What is carbon neutrality?
Carbon neutrality refers to the calculation of the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions produced directly or indirectly by enterprises, groups or individuals within a certain period of time, and then through afforestation, energy saving and emission reduction, etc., to offset their own carbon dioxide emissions to achieve "zero carbon dioxide emissions".
What is Carbon Sink?
Carbon Sink: Generally refers to the process, activity, and mechanism of removing carbon dioxide from the air. It mainly refers to the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed and stored by the forest, or the capacity of the forest to absorb and store carbon dioxide.
Research data shows that my country’s carbon sink capacity is gradually improving. Through vigorously cultivating and protecting plantations, my country’s terrestrial ecosystems will absorb approximately 1.11 billion tons of carbon annually from 2010 to 2016, and absorb 45% of human-made carbon emissions during the same period. Forestry Carbon sinks play an important role in the vision of carbon neutrality, and carbon sink projects will help our country achieve carbon neutrality goals.
What is Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS)?
Carbon capture, utilization and storage is abbreviated as CCUS, which is a technology that captures and purifies the carbon dioxide emitted during the production process, and then puts it into a new production process for recycling or storage. Among them, carbon capture refers to the collection of carbon dioxide generated by emission sources such as large power plants, steel plants, and cement plants, and storing them in various ways to prevent them from being emitted into the atmosphere.
This technology has the synergy of achieving large-scale greenhouse gas emission reduction and low-carbon utilization of fossil energy, and is one of the important technological choices for the global response to climate change in the future.
What is the carbon emission right (CER)?
Carbon emission rights are the origin of the Certification Emission Reduction (CER). In 2005, with the entry into force of the Kyoto Protocol, carbon emission rights became an international commodity. The subject of carbon emissions trading is called "Certified Emission Reduction (CER)".
Where do emission rights come from? The quota primary market and secondary market coexist.
What is carbon trading?
Carbon trading refers to carbon dioxide emission rights as a commodity. The buyer obtains a certain amount of carbon dioxide emission rights by paying a certain amount to the seller, thus forming a carbon dioxide emission right transaction.
The carbon trading market is a market artificially created by the government through the control of emissions from energy-consuming enterprises. Under normal circumstances, the government determines a total amount of carbon emissions and allocates carbon emission allowances to enterprises according to certain rules. If the company's emissions are higher than the quota in the future, it needs to buy the quota on the market. At the same time, some companies can sell excess allowances through the carbon trading market if their carbon emissions are lower than their quotas through the use of energy-saving and emission-reduction technologies. The two parties generally trade through carbon emission exchanges.
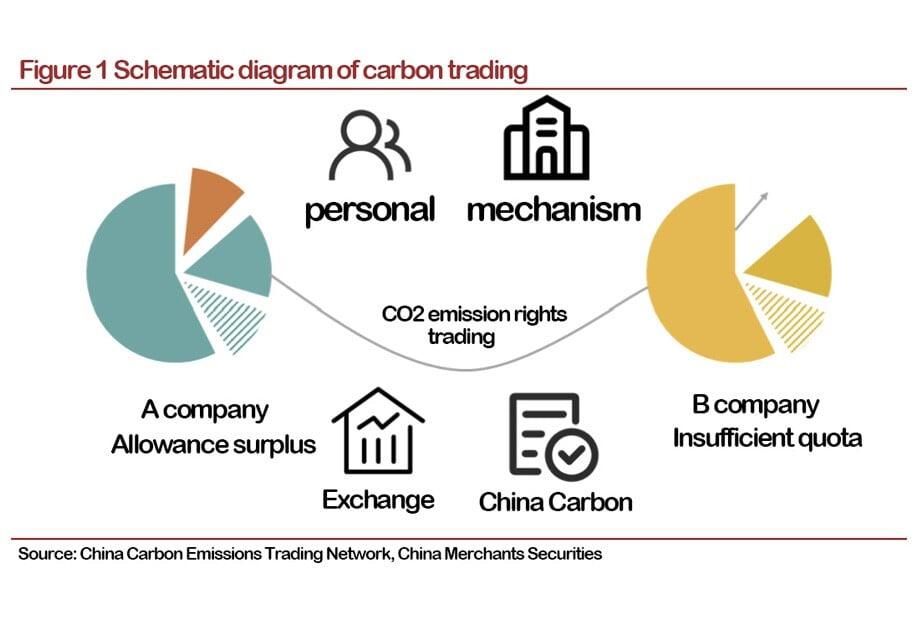
In the first case, if the company's emission reduction costs are lower than the carbon trading market price, the company will choose to reduce emissions, and the share of emission reductions can be sold for profit;
In the second case, when the cost of reducing emissions is higher than the carbon market price, companies will choose to purchase allowances from governments, enterprises, or other market entities in the carbon market to achieve the emission reduction targets set by the government. If the allowances are not purchased in sufficient quantities to cover their actual emissions, they will face high fines.
Through this set of design, the carbon trading market internalizes carbon emissions as part of the operating costs of enterprises, and the carbon emission price formed by the transaction guides enterprises to choose the most cost-effective carbon reduction methods, including energy saving and emission reduction transformation, carbon allowance purchase, Or carbon capture, etc., the market-oriented approach enables the transformation of the industrial structure from high energy consumption to low energy consumption while maintaining the optimization of emission reduction costs for the whole society.
What are carbon emission allowances and voluntary emission reductions (CCER)?
According to the classification of carbon trading, there are currently two types of basic products in my country's carbon trading market, one is the carbon emission allowance allocated by the government to enterprises, and the other is the certified voluntary emission reduction (CCER).
According to the "Measures for the Management of Carbon Emission Trading (Trial)" issued in December 2020, CCER refers to the quantitative verification of the greenhouse gas emission reduction effects of renewable energy, forestry carbon sinks, methane utilization and other projects in my country, and the amount of greenhouse gas emission reductions registered in the national voluntary emission reduction transaction registration system.
The first type, quota trading is a policy measure adopted by the government to complete the emission control target, that is, within a certain space and time, the emission control target is converted into carbon emission quotas and allocated to lower-level governments and enterprises. If the actual carbon emissions are less than the quota allocated by the government, companies can trade surplus carbon allowances to achieve a reasonable allocation of carbon allowances among different enterprises, and finally achieve the emission control target at a relatively low cost.
The second category, as a supplement introduces voluntary emission reduction market transactions outside the quota market, that is, CCER transactions. The CCER transaction alleges that emission companies purchase certified amounts that can be used to offset their own carbon emissions from companies that implement "carbon offset" activities.
"Carbon offset" refers to activities used to reduce greenhouse gas emission sources or increase greenhouse gas absorption sinks to compensate or offset greenhouse gas emissions from other emission sources, that is, the carbon emissions of companies that control emissions can be cleaned by non-emission control companies. Energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions or increases carbon sinks to offset it. Offset credits are issued after the emission reductions are obtained through the implementation of specific emission reduction projects, including renewable energy projects and forest carbon sink projects.
The carbon market gives CCERs to replace carbon emission allowances at a ratio of 1:1, that is, 1 CCER is equivalent to 1 allowance, which can offset 1 ton of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions. The "Carbon Emissions Trading Management Measures (Trial)" stipulates that key emission units are annually The national certified voluntary emission reductions can be used to offset the payment of carbon emission allowances, and the offset ratio shall not exceed 5% of the carbon emission allowances that should be paid.

